Setting a Baseline Run
The "Baseline Run" is a core concept in DBNL that, appropriately, refers to the Run used as a baseline when executing a Test Session. Conversely, the Run being tested is called the "Experiment Run". Any tests you've created that compare statistics will test the values in the experiment relative to the baseline.
Dynamic Baseline (Run Queries)
Depending on your use case, you may want to make your Baseline Run dynamic. You can use a Run Query for this. Currently, DBNL supports setting a Run Query that looks back a number of previous runs. For example, in a production testing use case, you may want to use the previous Run as the baseline for each Test Session, so you'd create a Run Query that looks back 1 run. See the UI example in the Setting a Default Baseline Run section for information on how to create a Run Query. You can also create a Run Query via the SDK.
Setting a Default Baseline Run
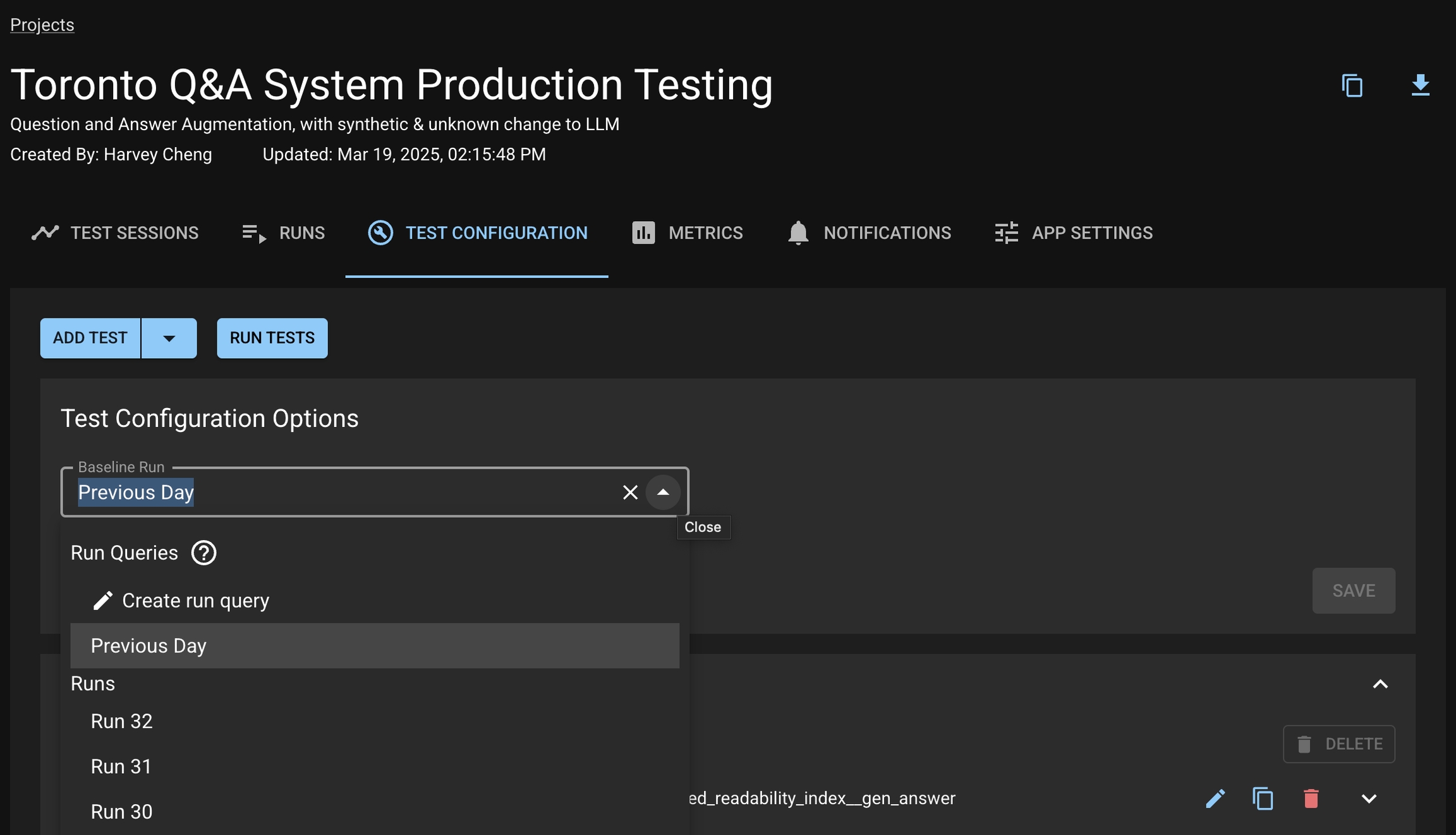
You can set a default Baseline Run to be used in all Test Sessions either via the UI or the SDK. Additionally, you can create a Run Query to make your Baseline Run dynamic for each Test Session.
From your Project, click the "Test Configuration" tab. Choose a Run or Run Query from the Baseline Run dropdown.
Was this helpful?

