Stages in the AI Software Development Lifecycle
Key Stages in the AI Development Lifecycle
The AI Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) differs from the traditional SDLC in that organizations typically progress through these stages in cycles, rather than linearly. A GenAI project might start with rapid prototyping in the Build phase, circle back to Explore for data analysis, then iterate between Build and Deploy as the application matures.
The unique challenges of AI systems require a specialized approach to testing throughout the entire life cycle. Testing happens across four key stages, each addressing different aspects of AI behavior: Explore, Build, Deploy, and Observe.
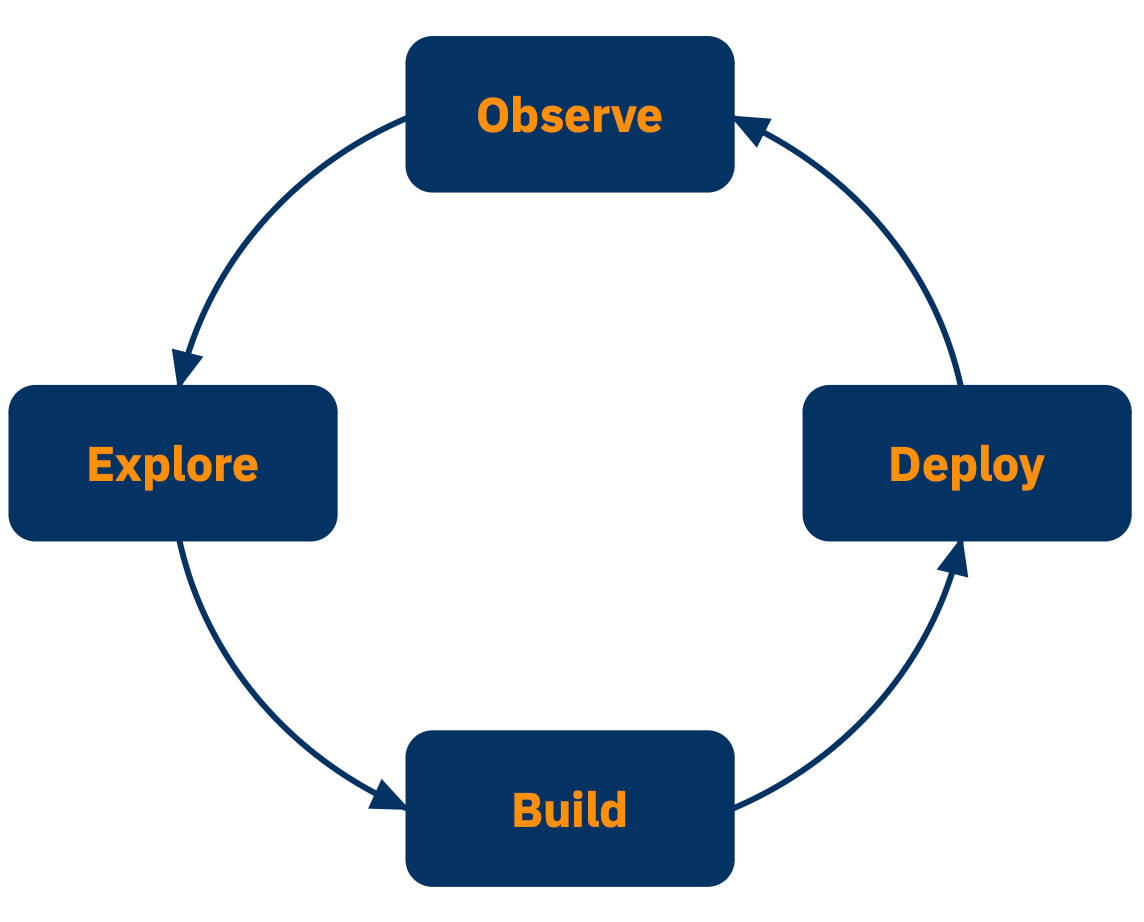
Explore - The identification and isolation of motivating factors (often business factors) which have inspired the creation/augmentation of the AI-powered app.
Build - Iteration through possible designs and constraints to produce something viable.
Deploy - The process of converting the developed AI-powered app into a service which can be deployed robustly.
Observe - Continual review and analysis of the behavior/health of the AI-powered app, including notifying interested parties of discordant behavior and motivating new Build goals. Without continuous feedback from the Observe phase, there’s a substantial risk that the application does not behave as expected - for example, the output of an LLM could provide nonsensical or incorrect responses. Additionally, the performance of the application degrades over time as the distributions of the input data shifts.
Testing Across the AI SDLC

Existing AI reliability methods - such as evaluations and monitoring - play crucial roles in the AI SDLC. However, they often focus on narrow aspects of reliability. AI testing, on the other hand, encompasses a more comprehensive approach, ensuring models behave as expected before, during, and after deployment.
Distributional is designed to help continuously ask and answer the question “Is my AI-powered app performing as desired?” In pursuit of this goal, we consider testing at three different elements of this lifecycle.
Production testing: Testing actual app usages observed in production to identify any unsatisfactory or unexpected app behavior.
This occurs during the Observe step.
Deployment testing: Testing the app currently deployed with a fixed (a.k.a. golden) dataset to identify any nonstationary behavior in components of the app (e.g., a third party LLM.)
This occurs during the Deploy step and in the arrow to the Observe step
Development testing: Testing new app versions on a chosen dataset to confirm that bugs have been fixed or improvements have been implemented.
This occurs between Build and Deploy.
Was this helpful?

